Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Konno, Chikara
JAEA-Conf 2023-001, p.143 - 146, 2024/02
I modified NJOY2016.67 to produce photonuclear ACE files which can be used in MCNP6.2 and PHITS3.27 and produced the ACE file of the JENDL-5 photonuclear sub-library. Simple test calculations with the produced ACE file supported that the produced ACE file had no serious problems.
Pyeon, C. H.*; Katano, Ryota; Oizumi, Akito; Fukushima, Masahiro
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 197(11), p.2902 - 2919, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sample reactivity and void reactivity experiments are carried out in the solid-moderated and solid-reflected cores at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA) with the combined use of aluminum (Al), lead (Pb) and bismuth (Bi) samples, and Al spacers simulating the void. MCNP6.2 eigenvalue calculations together with JENDL-4.0 provide good accuracy of sample reactivity with the comparison of experimental results; also experimental void reactivity is attained by using MCNP6.2 together with JENDL-4.0 and ENDF/B-VII.1 with a marked accuracy of relative difference between experiments and calculations. Uncertainty quantification of sample reactivity and void reactivity is acquired by using the sensitivity coefficients based on MCNP6.2/ksen and covariance library data of SCALE6.2 together with ENDF/B-VII.1, arising from the impact of uncertainty induced by Al, Pb and Bi cross sections. A series of reactivity analyses with the Al spacer simulating the void demonstrates the means of analyzing the void in the solid-moderated and solid-reflected cores at KUCA
Konno, Chikara; Ota, Masayuki*; Kwon, Saerom*; Onishi, Seiki*; Yamano, Naoki*; Sato, Satoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1046 - 1069, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:98.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)JENDL-5 was validated from a viewpoint of shielding applications under the Shielding Integral Test Working Group of the JENDL Committee. The following benchmark experiments were selected: JAEA/FNS in-situ experiments, Osaka Univ./OKTAVIAN TOF experiments, ORNL/JASPER sodium experiments, NIST iron experiment and QST/TIARA experiments. These experiments were analyzed with MCNP and nuclear data libraries (JENDL-5, JENDL-4.0 or JENDL-4.0/HE, ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JEFF-3.3). The analysis results demonstrate that JENDL-5 is comparable to or better than JENDL-4.0 or JENDL-4.0/HE, ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JEFF-3.3.
Maruyama, Yu; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki*; Shimada, Asako; Lind, T.*; Bentaib, A.*; Sogalla, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Albright, L.*; Clayton, D.*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4782 - 4795, 2023/08
Kimura, Yoshiki; Tsuchiya, Kenichi*
Radioisotopes, 72(2), p.121 - 139, 2023/07
Rapid and precise radioisotope identification in the scene of nuclear detection and nuclear security incidents is one of the challenging issues for the prompt response on the detection alarm or the incidents. A radioisotope identification algorithm using a deep artificial neural network model applicable to handheld gamma-ray detectors has been proposed in the present paper. The proposed algorithm automatically identifies gamma-emitting radioisotopes based on the count contribution ratio (CCR) from each of them estimated by the deep artificial neural network model trained by simulated gamma-ray spectra. The automated radioisotope identification algorithm can support first responders of nuclear detection and nuclear security incidents without sufficient experience and knowledge in radiation measurement. The authors tested the performance of the proposed algorithm using two different types of deep artificial neural network models in application to handheld detectors having high or low energy resolution. The proposed algorithm showed high performance in identifying artificial radioisotopes for actually measured gamma-ray spectra. It was also confirmed that the algorithm is applicable to identifying  U and automated uranium categorization by analyzing estimated CCRs by the deep artificial neural network models. The authors also com-pared the performance of the proposed algorithm with a conventional radioisotope identification method and discussed promising ways to improve the performance of the algorithm using the deep artificial neural network.
U and automated uranium categorization by analyzing estimated CCRs by the deep artificial neural network models. The authors also com-pared the performance of the proposed algorithm with a conventional radioisotope identification method and discussed promising ways to improve the performance of the algorithm using the deep artificial neural network.
Tazaki, Makiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(3), p.183 - 186, 2023/03
, 65(3), p.183 - 186, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-053, 89 Pages, 2023/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Uncertainty reduction of the FPs transport mechanism and debris degradation behavior and evaluation of the reactor contamination of debris state on the basis of the accident progression scenario of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 2 and 3" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to elucidate the cause of the high dosage under shield plug by clarification of to the cesium behavior of migration, adhesion to structure and deposition as well as evaluate the properties of metal-rich debris predeceasing melted through the materials science approach based on the most probable scenario of accident progression of Unit 2 and 3. In this fiscal year, the followings were achieved.
Sato, Takumi; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki; Quaini, A.*; Gu neau, C.*
neau, C.*
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 79, p.102481_1 - 102481_11, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Thermodynamics)Ho, H. Q.; Ishii, Toshiaki; Nagasumi, Satoru; Ono, Masato; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Goto, Minoru; Simanullang, I. L.*; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 396, p.111913_1 - 111913_9, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ho, H. Q.; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
Recent Contributions to Physics, 82(3), p.16 - 20, 2022/09
Nagata, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Omori, Takazumi; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2022-017, 113 Pages, 2022/08
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) was decided as a one of decommission facilities in April 2017. The activation activity of radioactive materials remaining in the reactor facility was evaluated in order to submit the decommissioning plan to the Nuclear Regulation Authority. Total activation activity was 9.3 10
10 Bq after the permanent shutdown of reactor, 2.7
Bq after the permanent shutdown of reactor, 2.7 10
10 Bq after 21 years, 1.0
Bq after 21 years, 1.0 10
10 Bq after 40 years and 2.4
Bq after 40 years and 2.4 10
10 Bq after 100 years. The structure with high activation activity was the core structural materials in JMTR such as beryllium frame, aluminum reflector, etc., and the material was stainless steel, beryllium, etc. The ratio of nuclides to the total amount of activated radioactivity was highest in H-3 until about 40 years after the reactor shutdown, and then in Ni-63. For reference, the radioactivity level was classified based on the results of the obtained radioactivity concentration. The ratio of the weight of each radioactivity level to the total weight was 0.3-0.4% (10-13t) for L1, 0.0-0.4% (0-14t) for L2, 1.0-1.2% (32-39t) for L3 and 98.0-98.7% (about 3200t) for CL until 100 years after the reactor shutdown. It was found that those classified as CL account for more than 90% of the total. When treating and disposing of radioactive waste, evaluation will be carried out based on appropriate methods, including evaluation results of secondary pollutants.
Bq after 100 years. The structure with high activation activity was the core structural materials in JMTR such as beryllium frame, aluminum reflector, etc., and the material was stainless steel, beryllium, etc. The ratio of nuclides to the total amount of activated radioactivity was highest in H-3 until about 40 years after the reactor shutdown, and then in Ni-63. For reference, the radioactivity level was classified based on the results of the obtained radioactivity concentration. The ratio of the weight of each radioactivity level to the total weight was 0.3-0.4% (10-13t) for L1, 0.0-0.4% (0-14t) for L2, 1.0-1.2% (32-39t) for L3 and 98.0-98.7% (about 3200t) for CL until 100 years after the reactor shutdown. It was found that those classified as CL account for more than 90% of the total. When treating and disposing of radioactive waste, evaluation will be carried out based on appropriate methods, including evaluation results of secondary pollutants.
 , Zr, and stainless-steel
, Zr, and stainless-steelKirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 567, p.153842_1 - 153842_15, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To understand the chemical structure and stability of nuclear fuel debris consisting of UO , Zr, and Stainless Steel (SUS) generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in Japan in 2011, simulated debris of the UO
, Zr, and Stainless Steel (SUS) generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in Japan in 2011, simulated debris of the UO -SUS-Zr system and other fundamental component systems were synthesized and characterized. The simulated debris were synthesized by heat treatment for 1 to 12 h at 1600
-SUS-Zr system and other fundamental component systems were synthesized and characterized. The simulated debris were synthesized by heat treatment for 1 to 12 h at 1600 C, in inert (Ar) or oxidative (Ar + 2% O
C, in inert (Ar) or oxidative (Ar + 2% O ) atmospheres.
) atmospheres.  Np and
Np and  Am tracers were doped for the leaching tests of these elements and U from the simulated debris. The characterization of the simulated debris was conducted by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman spectroscopy, and M
Am tracers were doped for the leaching tests of these elements and U from the simulated debris. The characterization of the simulated debris was conducted by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman spectroscopy, and M ssbauer spectroscopy, which provided the major uranium phase of the UO
ssbauer spectroscopy, which provided the major uranium phase of the UO  -SUS-Zr debris was the solid solution of U
-SUS-Zr debris was the solid solution of U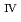 O
O (s.s.) with Zr(IV) and Fe(II) regardless of the treatment atmosphere. The long-term immersion test of the simulated debris in pure water and that in seawater revealed the macro scale crystal structure of the simulated debris was chemically very stable in the wet condition for a year or more. Furthermore, the leaching test results showed that the actinide leaching ratios of U, Np, Am from the UO
(s.s.) with Zr(IV) and Fe(II) regardless of the treatment atmosphere. The long-term immersion test of the simulated debris in pure water and that in seawater revealed the macro scale crystal structure of the simulated debris was chemically very stable in the wet condition for a year or more. Furthermore, the leaching test results showed that the actinide leaching ratios of U, Np, Am from the UO -SUS-Zr debris were very limited and less than 0.08 % for all the experiments in this study.
-SUS-Zr debris were very limited and less than 0.08 % for all the experiments in this study.
Kochiyama, Mami; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2022-009, 56 Pages, 2022/06
It is necessary to evaluate radioactivity inventory in wastes before disposal of low-level radioactive wastes generated from dismantling research reactors. It is efficient for owners of each research reactor to use a common radioactive evaluation method in order to comply with the license application for disposal facility. In this report, neutron transport and activation calculations were carried out for the Rikkyo University research reactor in order to examine a common radioactivity evaluation method for burial disposal of radioactive wastes generated by dismantling. We adopted the neutron transport codes DORT and MCNP and the activation code ORIGEN-S with cross-section libraries based on JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/AD-2017. The radioactivity concentrations obtained by the radiochemical analysis and both calculation codes were in agreement by 0.4 to 3 times. Therefore, by appropriately considering this difference, the radioactivity evaluation method by DORT, MCNP and ORIGEN-S can be applied to the radioactivity evaluation for buried disposal. In order to classify wastes from dismantling by clearance or buried disposal method according to their radioactivity levels, we also created radioactivity concentration distributions in the concrete area and graphite thermal column area.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-010, 155 Pages, 2022/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of the technology for preventing radioactive particles' dispersion during the fuel debris retrieval" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to clarify the behavior of microparticles in gas and liquid phases in order to steadily confine radioactive microparticles during fuel debris retrieval in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, TEPCO. As measures to prevent dispersion of microparticles, (1) a method to suppress the dispersion with minimum amount of water utilizing water spray etc., and (2) a method to suppress the dispersion by solidifying ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-009, 73 Pages, 2022/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Basic research on the stability of fuel debris including alloy phase" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study focus on fuel debris consisting of oxide phase and alloy phase generated by the high temperature chemical reaction between structure materials (SUS pipes, pressure vessels, etc.) and fuels (melted fuels, claddings components, etc.). We synthesize the simulated debris of UO -SUS system and UO
-SUS system and UO -Zr(ZrO
-Zr(ZrO )-SUS system by high-temperature heat treatment, and measure their chemical property and dissolution behavior in water.
)-SUS system by high-temperature heat treatment, and measure their chemical property and dissolution behavior in water.
Hidaka, Akihide
Nuclear Technology, 208(2), p.318 - 334, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)The author previously proposed that the Cs bearing microparticle (Type A) may have been formed by melting and atomization of glass fibers (GF) of the HEPA filter in the SGTS due to flame and blast during the hydrogen explosion in Unit 3. If this hypothesis is correct, the Type A could contain or accompany carbon (C), that ignites spontaneously above 623 K, because of the limited time to be heated up, inclusion of C in the binder applied on the GF surface and closely located charcoal filter. As the previous studies did not focus on C, the present analyses were performed with EPMA whether the Type A contains C. The results showed that the Type A contained C originating from the binder, and non-spherical particles accompanied by the Type A and the film surrounding the Type A contained more C, which is thought to originate from the charcoal filter. These results cannot be explained by the other mechanisms proposed so far, and can be explained consistently by the author proposed hypothesis.
Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Tada, Kenichi; Ho, H. Q.; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nagasumi, Satoru; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 158, p.108270_1 - 108270_8, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tazaki, Makiko; Shimizu, Ryo; Kimura, Takashi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Suda, Kazunori
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/08
Inoue, Naoko; Noro, Naoko; Kawakubo, Yoko; Sekine, Megumi; Okuda, Masahiro; Hasegawa, Nobuhiko*; Naoi, Yosuke
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/08
Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Nonproliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) celebrated its 10th anniversary in December 2020. One of its pillars is capacity building support mainly to Asian countries. 183 trainings were implemented with more than 4,600 participants since its establishment, however, the COVID-19 pandemic impacted in the implementation of the trainings. ISCN/JAEA has started to develop the online trainings since April 2020, and implemented two regional trainings, Physical Protection and State System of Accounting for and Control (SSAC) for IAEA Safeguards in October and November 2020, respectively. The efforts continue in further development of trainings/workshops, including the regional training on Additional Protocol for IAEA Safeguards Agreement Commodity Identification Training, and other two national workshops with foreign instructors. Online training can provide not only training opportunities for those who have difficulty in traveling for security and safety reasons including under the travel restriction by COVID-19 pandemic, but also could serve in making them more effective and efficient, especially by the combination with in-person trainings. The pandemic, as a result, accelerate ISCN/JAEA to develop and implement the online trainings, which key is the international collaboration with the partners including IAEA, DOE/NNSA and Sandia National Laboratories and International Nuclear Nonproliferation and Security Academy (INSA) of the Korea Institute of Nuclear Nonproliferation and Control (KINAC). This paper will provide the efforts of ISCN/JAEA how to address the online training development and implementation, current status, lesson learned, and future plan.
Ichihara, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Naohiro*; Moritani, Hiroshi*; Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi
Frontiers in Built Environment (Internet), 7, p.676408_1 - 676408_14, 2021/06
The objective of this study is the improvement of response evaluations of structures, facilities and equipment in evaluation of three-dimensional seismic behavior of nuclear power plant facilities, by three-dimensional finite element method model, including separation and sliding between the soil and the basement walls. To achieve this, simulation analyses of Kashiwazaki Kariwa nuclear power plant unit 7 reactor building under the 2007 Niigataken-chuetsu-oki earthquake event were carried out. These simulation analyses consider soil-structure interaction using a three-dimensional finite element method model in which the soil and building are three-dimensionally modeled by the finite element method. It is found that basemat uplift is generated on east side of the basemat edge, and this has an important influence on the results. The importance is evidenced by the difference of local response in soil pressure characteristics beneath the edge of basemat, the soil pressure characteristics along the east side of basement wall and the maximum acceleration response at the west end of the embedded surface. Although, in this particular study, basemat uplift, separation and sliding have only a relatively small influence on the maximum acceleration response of embedded surface and the soil pressure characteristics along the basement walls and beneath the basemat, under strong earthquake motion, these influences can be significant, therefore appropriate evaluation of this effect should be considered.